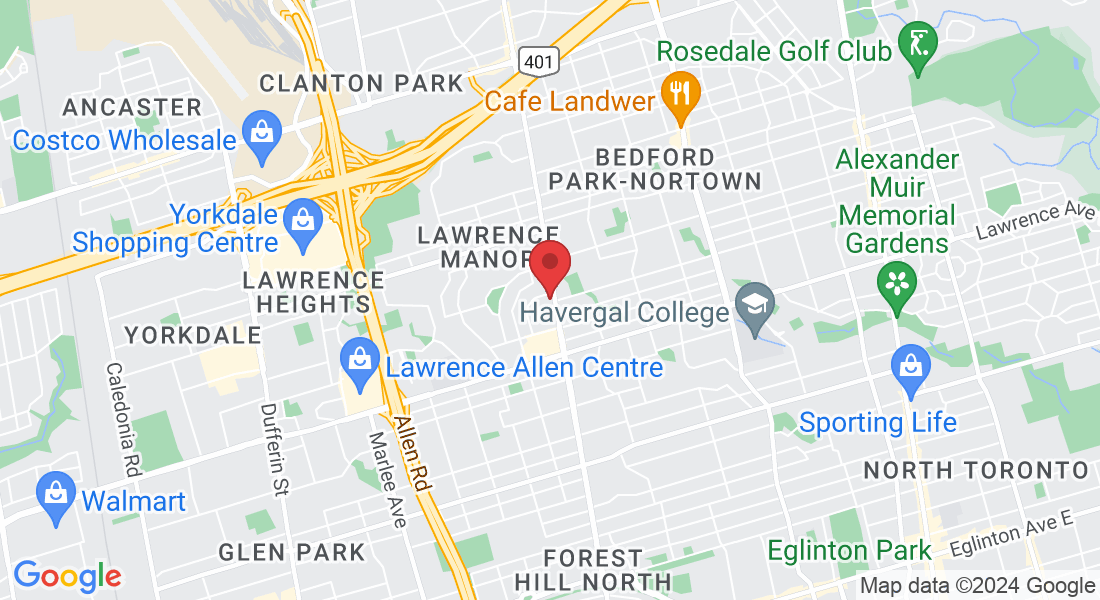
BETTER POSTURE FOR BETTER HEALTH
What is good posture?
Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing, sitting or lying down. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit and lie in positions where the least strain is placed on supporting muscles and ligaments during movement or weight-bearing activities. Maintaining good posture involves training your body to move and function where the least strain is placed on the body. Good posture improves the physiologic function of your body, while improving your appearance. To maintain proper posture, you need to have adequate muscle flexibility and strength, normal joint motion in the spine and other body regions, as well as efficient postural muscles that are balanced on both sides of the spine. In addition, you must recognize your postural habits at home and in the workplace and work to correct them, if necessary. Your posture has a positive or negative influence on the daily activities that you do. Good posture demonstrates confidence, balance, pain free movement and enhanced physiologic function of your body. Whereas poor posture causes additional stress to the body, spinal degeneration, and diffuse pain. Simply correcting your posture can enhance the quality of your life and overall health. Good posture promotes movement efficiency and endurance and contributes to an overall feeling of wellbeing. The return on investment for better posture will be astounding in later years. We simply cannot afford to neglect our postural needs, especially when so much of our ability to function is riding on the quality of our postural alignment.
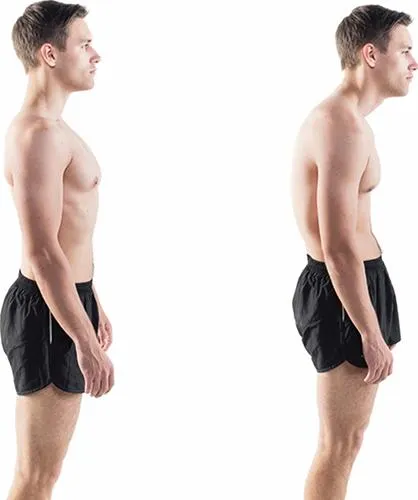
A HEALTHY BACK HAS THREE NATURAL CURVES:
An inward or forward curve at the neck (cervical curve) An outward or backward curve at the upper back (thoracic curve) An inward curve at the lower back (lumbar curve) Good posture helps maintain these natural curves, while poor posture does the opposite – which can stress or pull muscles and cause pain.
THE ANATOMY OF GOOD POSTURE:
Your Spine: Good posture actually means keeping the three curves of your spine in balanced alignment. Misalignments of the vertebrae, or spinal subluxations, cause postural abnormalities. Your Muscles. Strong and flexible muscles also are essential to good posture. Abdominal, hip, and leg muscles that are weak and inflexible cannot 4 support your back’s natural curves. Your Joints. Hip, knee, and ankle joints balance your back’s natural curves when you move, making it possible to maintain good posture in any position.
PROPER POSTURE IS A KEY COMPONENT TO OPTIMAL HEALTH AND WELLNESS POSTURE?
Perhaps the most important benefit of good posture is that it improves function of the internal organs. When the body is in a slouched forward position (head and shoulders rolled forward), our rib cage is actually pushing down on our internal organs. Common short-term effects are muscular soreness, neck pain, and headaches. Long- term effects include: decreased respiratory capacity, digestive problems, and migraines. If postural imbalances go uncorrected, further consequences may occur throughout the body, such as: spinal degeneration, muscle soreness, and arthritic joints.
THE BENEFITS OF PROPER POSTURE
- Keeps bones and joints in the correct alignment so that muscles are being used properly and efficiently.
- Helps decrease the abnormal wearing of joint surfaces that could result in arthritis.
- Decreases the stress on the ligaments holding the joints of the spine together.
- Optimizes breathing and circulation
- Prevents the spine from becoming fixed in abnormal positions (for example an abnormal lateral curvature, or scoliosis).
- Prevents fatigue because muscles are being used more efficiently, allowing the body to use less energy.
- Improves organ function. American Posture Institute Page 3 Prevents strain or overuse problems.
- Prevents backache, neck pain, and diffuse muscular pain.
- Contributes to a good appearance.
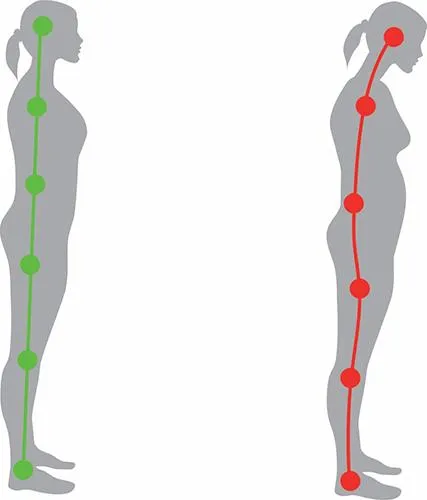
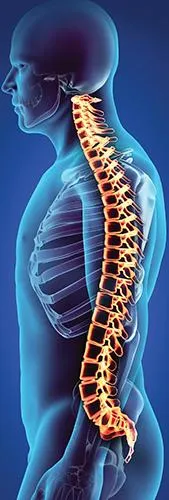
CONSEQUENCES OF POOR POSTURE
Good posture is also good prevention. Poor posture can lead to excessive strain on our postural muscles and may even cause them to relax, when held in certain positions for long periods of time. For example, you can typically see this in people who bend forward at the waist for a prolonged time in the workplace. Their postural muscles are more prone to injury and back pain. Several factors contribute to poor posture-most commonly, stress, obesity, pregnancy, weak postural muscles, abnormally tight muscles, and high-heeled shoes. In addition, decreased flexibility, a poor work environment, incorrect working posture, and unhealthy sitting and standing habits can also contribute to poor body positioning.
Our Patients Thrive.
Request an Appointment
Choose an option and then select an appointment date and time that works best for you. We will review your request and then reach out to confirm your appointment.
Office Hours
SUNDAY
9:30a - 1:30p
MONDAY
9:00a - 12:00p, 1:00p - 3:00p, 4:00p - 6:30p
TUESDAY
9:00a - 11:00a
WEDNESDAY
9:00a - 1:00p, 3:00p - 6:00p
THURSDAY
1:30p - 3:00p. 4:00p - 7:30p
FRIDAY
9:00a - 1:30p
Didn't see an appointment time that works for you? Send us a message.
Office Hours
Sunday: 9:30a - 1:30p
Monday: 9:00a - 12:00p, 1:00p - 3:00p, 4:00p - 6:30p
Tuesday: 9:00a - 11:00a
Wednesday: 9:00a - 1:00p, 3:00p - 6:00p
Thursday: 1:30p - 3:00p. 4:00p - 7:30p
Friday: 9:00a - 1:30p